Feed Up
(→Setting SMART Goals) |
(→SOLO Visual Maps) |
||
| (36 intermediate revisions by one user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | This wiki page describes how [[SOLO Taxonomy]] can be adapted for use with students and teachers to improve the effectiveness of '''“feed up”''' (Where am I going?). Other pages will explore "feedback" (How am I going?) and | + | __FORCETOC__ |
| + | This wiki page describes how [[SOLO Taxonomy]] can be adapted for use with students and teachers to improve the effectiveness of '''“feed up”''' (Where am I going?). Other pages will explore "[[Feed Back|feedback]]" (How am I going?) and “[[Feed Forward|feed forward]]” (What should I do next?). | ||
| Line 7: | Line 8: | ||
{| style="width: 500px" border="1" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" | {| style="width: 500px" border="1" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | ! scope="col" | Feed Up | + | ! scope="col" style= "background-color: yellow;"| Feed Up |
! scope="col" | Feed Back | ! scope="col" | Feed Back | ||
! scope="col" | Feed Forward | ! scope="col" | Feed Forward | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Where am I going? | + | | style= "background-color: yellow;"|Where am I going? |
| How am I going? | | How am I going? | ||
| Where to next? | | Where to next? | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | Be explicit about the learning task and success criteria. Set appropriate, challenging and specific goals,Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO),Learning Intentions (LI). | + | | style= "background-color: yellow;"| Be explicit about the learning task and success criteria. Set appropriate, challenging and specific goals,Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO),Learning Intentions (LI). |
| Self assess progress against the success criteria. | | Self assess progress against the success criteria. | ||
| Set next learning steps. | | Set next learning steps. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |style= "background-color: yellow;"| |
We are learning to ... (WALT), I am learning to ... (IALT) | We are learning to ... (WALT), I am learning to ... (IALT) | ||
| Line 27: | Line 28: | ||
| My next step is to .... | | My next step is to .... | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | | style= "background-color: yellow;"| |
Effort and effective strategies. | Effort and effective strategies. | ||
| Line 37: | Line 38: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == '''Feed Up: Identifying the learning goals/intentions''' == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Teaching and learning goals focus on declarative knowledge and functioning knowledge. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Check out the new [http://pamhook.com/free-resources/learning-intention-generator/ HookED SOLO Learning Intention Generator]''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Identifying ‘explicit’ learning goals can be challenging to teachers. Yet without ‘explicit’ learning goals, feedback cannot be wholly effective. | ||
| + | |||
| + | SOLO is used as a model of different levels of understanding when planning learning intentions by teachers (and students). The process of ‘constructive alignment’ uses learning verbs coded against SOLO outcomes to unpack New Zealand Curriculum achievement objectives and achievement standards(Biggs and Tang, 2009, p50). | ||
| + | |||
| + | Associating the levels in SOLO with “declarative knowledge verbs” (Biggs & Tang, 2007, p79) has been fundamental to building clarity, competence and confidence into the process of writing learning goals. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In New Zealand the list of SOLO coded learning verbs for declarative knowledge and functioning knowledge (see table 1 below)have been selected from commonly used task descriptors in NCEA (Hook, 2011) and chosen to support a classroom based approach to SOLO Taxonomy. As such they differ from the classification of learning verbs by Biggs and Tang 2007. Refer Table 2 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Table 1: SOLO Learning Verbs (HookED classroom based approach) | ||
| + | {| style="width: 500px" border="1" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | SOLO Levels | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Learning Verbs/Task Descriptors | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Unistructural | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Define, identify, name, draw, find, label, match | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Multistructural | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Describe, list, outline, follow a procedure | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Relational | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Sequence, classify, compare and contrast, explain causes, explain effects, analyse, make an analogy, organise, distinguish, interview, question | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Extended Abstract | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Generalise, predict, evaluate, reflect, hypothesise, create, prove, plan, justify, argue, compose, prioritise, design, construct, perform | ||
| + | |||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Verbs typical of each level in SOLO Taxonomy''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | My alignment of the verbs with the SOLO levels, is a little different from that suggested by Biggs in Table 2 below. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If you check Biggs and Tang - Figure 5.2. A hierarchy of verbs that may be used to form intended learning outcomes p.79 and table 5.1.Some verbs for ILOs from the SOLO taxonomy p.80 you will see that I have shifted Biggs’ verbs to better suit a classroom based approach. | ||
| + | I wanted to make the connection between the verb and the SOLO level explicit – verbs for bringing in loose ideas, verbs for connecting ideas and verbs for extending ideas. | ||
| + | For example, when I developed the classroom based approach for use by students as young as five years old - I shifted classify and sequence to relational because it seemed like the process of sequencing and classifying involved students in making connections between ideas. The SOLO relational visual maps and self-assessment rubrics reinforced this. I moved predict, conclude, summarise, make a plan to the extended abstract level because they seemed to involve students in looking at connected ideas in a new way. The SOLO extended abstract visual maps and self-assessment rubrics reinforced this. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Prof. John Biggs has recognised the changes I made in the development of a classroom based approach to using SOLO – and given his blessing. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Context is important in aligning verbs to SOLO outcomes in Biggs and Tang (2007) John notes | ||
| + | ''“Some verbs could be either extended abstract or relational, depending on, for example,, the degree of originality or the context in which the verb was deployed: ‘solve a problem’, for example. And whether ‘paraphrase’ is relational or multistructural depends on how the student goes about paraphrasing: replacing with like-meaning phrases or rethinking the meaning of the whole text and rewriting it.”'' Biggs and Tang p80 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Table 2: Verbs/Task Descriptors Typical of each Level in SOLO Taxonomy | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| style="width: 500px" border="1" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | SOLO Levels | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Source – Biggs Website | ||
| + | http://www.johnbiggs.com.au/academic/solo-taxonomy/ | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Source - Biggs and Tang | ||
| + | Fig. 5.2 p.79 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Source - Biggs and Tang | ||
| + | Table 5.1 p.80 | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Classroom based approach | ||
| + | Source - Hooked on Thinking Wiki -SOLO Diagram and text | ||
| + | http://pamhook.com/wiki/The_Learning_Process | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Classroom based approach | ||
| + | Source - HookED Handouts and Presentations Publications - SOLO Verbs | ||
| + | www.pamhook.com | ||
| + | ! scope="col" | Classroom based approach | ||
| + | Source – HookED Learning Intention Generator | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Unistructural | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Identify, name, follow a simple procedure | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Identify, do simple procedure | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Memorise, identify, recognise, count, define, draw, find, label, match, name, quote, recall, recite, order, tell, write, imitate. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Define, identify, do simple procedure | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Define, identify, name, draw, find, label, match | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Define, name, find, match, identify draw, label recall | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Multistructural | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Combine, describe, enumerate, perform serial skills, list | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Enumerate, describe, list, combine, do algorithm | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Classify, describe, list, report, discuss, illustrate, select, narrate, compute, sequence, outline, separate | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Define, describe, do algorithm, combine | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Describe, list, outline, follow a procedure | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Describe, list, outline, follow a procedure | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Relational | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Analyse, apply, argue, compare and contrast, criticise, explain causes, relate, justify | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Compare, contrast, explain causes, analyse, relate, apply. | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Apply, integrate, analyse, explain, predict, conclude, summarise (précis), review, argue, transfer, make a plan, characterise, compare, contrast, differentiate, organise, debate, make a case, construct, review and rewrite, examine, translate, paraphrase, solve a problem | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Compare, contrast, explain causes, sequence, classify, analyse (part whole), relate, analogy, apply, formulate questions | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Sequence, classify, compare and contrast, explain causes, explain effects, analyse, make an analogy, organise, distinguish, interview, question | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Sequence, compare and contrast, explain effects, make an analogy. distinguish, question, classify, explain causes analyse, organise, interview, apply | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | Extended Abstract | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Create, formulate, generate, hypothesise, reflect, theorise | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Theorise, generalise, hypothesise, reflect | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Compose, invent, originate, prove from first principles, make an original case, solve from first principles | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Evaluate, theorise, generalise, predict, create, imagine | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Generalise, predict, evaluate, reflect, hypothesise, create, prove, plan, justify, argue, compose, prioritise, design, construct, perform | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | Generalise, evaluate, hypothesise, prove, justify, compose, design, perform, predict, reflect, create, plan, argue, prioritise, construct, invent | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == '''SOLO Visual Maps''' == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Visual mapping helps students understand the process steps when they are using academic language - describing, explaining, analysing , evaluating etc. | ||
| + | They are useful draft writing templates for both structure and content across different levels of SOLO tasks and outcomes. | ||
| + | |||
| + | When introducing the SOLO maps to students work with familiar content and contexts to reduce the cognitive load when learning a new process. Work for student fluency in map use. Give students many opportunities to use each map so they can "overlearn" the process steps for comparison, explanation etc. Encourage double processing whereby the student drafts thinking using the maps before writing AND also reads content from an existing text/paragraph and then summarise it onto a map. In time fluent users will be able to select an appropriate SOLO process map for an identified task. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Expert users will adapt and modify existing process maps to connect their draft thinking outcomes. For example - connecting a SOLO Explain effects map to a SOLO Sequence map. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Students can also be encouraged to build their own maps using the rectangle/speech bubble/thought bubble templates - [http://pamhook.com/2015/08/04/make-your-own-solo-maps/ as shown in this post] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
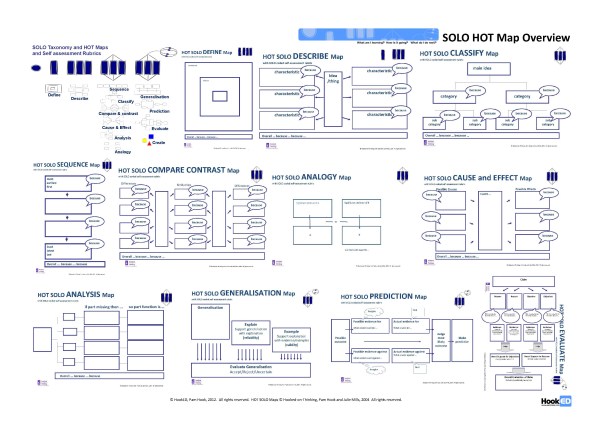
| + | '''A3 Poster - HOT SOLO Map Overview''' Download here | ||
| + | [[File: HookEDHOTMapsWordPoster_A3_1.pdf]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:HookEDHOTMapsWordPoster_A3_1 (600 x 424).jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Check out the following SOLO maps, self assessment rubrics and examples of student use:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| style="width: 500px" border="1" cellpadding="1" cellspacing="1" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''SOLO Multistructural Maps''' | ||
| + | | '''SOLO Relational Maps''' | ||
| + | | '''SOLO Extended Abstract Maps''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[HOT SOLO Define Map]] | ||
| + | | [[HOT SOLO Sequence Map]] | ||
| + | | [[HOT SOLO Generalise Map]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[HOT SOLO Describe Map]] | ||
| + | | [[HOT SOLO Classify Map]] | ||
| + | | [[HOT SOLO Predict Map]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | [[HOT SOLO Compare and Contrast Map]] | ||
| + | | [[HOT SOLO Evaluate Map]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | [[HOT SOLO Explain Map]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | [[HOT SOLO Analyse Map]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | [[HOT SOLO Analogy Map]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | [[HookED SOLO Explain Causes Map]] | ||
| + | | [[HookED Describe Plus Plus Map]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | [[HookED SOLO Explain Effects Map]] | ||
| + | | [[HookED SOLO Reflect Map]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | [[HookED Explain Author's Purpose Map]] | ||
| + | | [[HookED SOLO Make Meaning Map]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | [[HookED SOLO Analogy Map]] | ||
| + | | [[HookED SOLO Opinion Map]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |[[HookED SOLO Problem Solution Map]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | [[HookED SOLO Cycle Map]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | The HOT SOLO Maps are published in [http://www.essentialresources.co.nz/Products.aspx?SubjectID=0&SeriesID=SER5619 SOLO Taxonomy - A Guide for Schools Book 1]. Summary versions are available in the links above. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The HookED SOLO Maps are published here and in the following presentations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Hook, P. and Cassé, B. (2013). [http://www.essentialresources.co.nz/Products.aspx?SubjectID=0&SeriesID=SER5746SOLO Taxonomy in the Early Years. Making connections for belonging, being and becoming.] Essential Resources Educational Publishers Limited. New Zealand. | ||
| + | |||
| + | McNeill, L. and Hook, P. (2012). [http://www.essentialresources.co.nz/Products.aspx?SubjectID=0&SeriesID=SER5718 SOLO Taxonomy and Making Meaning. Book 1. Text purposes, audiences and ideas.] Essential Resources Educational Publishers Limited. New Zealand. | ||
| + | |||
| + | McNeill, L. and Hook, P. (2012). [http://www.essentialresources.co.nz/Products.aspx?SubjectID=0&SeriesID=SER5718 SOLO Taxonomy and Making Meaning. Book 2. Language features, structure and organisation.] Essential Resources Educational Publishers Limited. New Zealand. | ||
| + | |||
| + | McNeill, L. and Hook, P. (2012). [http://www.essentialresources.co.nz/Products.aspx?SubjectID=0&SeriesID=SER5718 SOLO Taxonomy and Making Meaning. Book 3. Extended texts and thematic studies.] Essential Resources Educational Publishers Limited. New Zealand. | ||
== '''Setting SMART Goals''' == | == '''Setting SMART Goals''' == | ||
| Line 47: | Line 280: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| '''Specific''' | | '''Specific''' | ||
| − | | Ask explicit focused questions. e.g. 5W and 1H questions | + | | Ask explicit focused questions. e.g. 5W and 1H questions |
| − | | | + | | Ask questions aligned to differentiated SOLO outcomes. E.g. Compare and contrast (Relational Outcome) |
|- | |- | ||
| '''Measurable''' | | '''Measurable''' | ||
| Establish specific criteria for measuring progress and knowing when a goal has been achieved. | | Establish specific criteria for measuring progress and knowing when a goal has been achieved. | ||
| − | | | + | | Establish SOLO differentiated success criteria for learning verbs. E.g. HOT SOLO Self assessment rubrics for learning verbs |
|- | |- | ||
| '''Attainable''' | | '''Attainable''' | ||
| − | | Develop differentiated sub-goals | + | | Develop differentiated sub-goals |
| − | | | + | | Establish SOLO differentiated success criteria for learning verbs. E.g. HOT SOLO Self assessment rubrics for learning verbs |
|- | |- | ||
| '''Realistic''' | | '''Realistic''' | ||
| − | | Able and motivated to achieve | + | | Able and motivated to achieve |
| − | | | + | | Use SOLO differentiated success criteria to establish level of pre-topic learning. |
|- | |- | ||
| '''Timely''' | | '''Timely''' | ||
| − | | Create timeline/Gantt chart | + | | Create timeline/Gantt chart |
| − | | | + | | Use SOLO differentiated success criteria for time management (Functioning knowledge) |
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{HookEDwiki navbar}} | ||
Latest revision as of 23:23, 17 January 2016
This wiki page describes how SOLO Taxonomy can be adapted for use with students and teachers to improve the effectiveness of “feed up” (Where am I going?). Other pages will explore "feedback" (How am I going?) and “feed forward” (What should I do next?).
Contents |
Overview
| Feed Up | Feed Back | Feed Forward |
|---|---|---|
| Where am I going? | How am I going? | Where to next? |
| Be explicit about the learning task and success criteria. Set appropriate, challenging and specific goals,Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO),Learning Intentions (LI). | Self assess progress against the success criteria. | Set next learning steps. |
|
We are learning to ... (WALT), I am learning to ... (IALT) |
I will know I am successful when ..., My learning outcome is ... because ... |
My next step is to .... |
|
Effort and effective strategies. |
Effort and effective strategies. |
Effort and effective strategies. |
Feed Up: Identifying the learning goals/intentions
Teaching and learning goals focus on declarative knowledge and functioning knowledge.
Check out the new HookED SOLO Learning Intention Generator
Identifying ‘explicit’ learning goals can be challenging to teachers. Yet without ‘explicit’ learning goals, feedback cannot be wholly effective.
SOLO is used as a model of different levels of understanding when planning learning intentions by teachers (and students). The process of ‘constructive alignment’ uses learning verbs coded against SOLO outcomes to unpack New Zealand Curriculum achievement objectives and achievement standards(Biggs and Tang, 2009, p50).
Associating the levels in SOLO with “declarative knowledge verbs” (Biggs & Tang, 2007, p79) has been fundamental to building clarity, competence and confidence into the process of writing learning goals.
In New Zealand the list of SOLO coded learning verbs for declarative knowledge and functioning knowledge (see table 1 below)have been selected from commonly used task descriptors in NCEA (Hook, 2011) and chosen to support a classroom based approach to SOLO Taxonomy. As such they differ from the classification of learning verbs by Biggs and Tang 2007. Refer Table 2
Table 1: SOLO Learning Verbs (HookED classroom based approach)
| SOLO Levels | Learning Verbs/Task Descriptors |
|---|---|
| Unistructural |
Define, identify, name, draw, find, label, match |
| Multistructural |
Describe, list, outline, follow a procedure |
| Relational |
Sequence, classify, compare and contrast, explain causes, explain effects, analyse, make an analogy, organise, distinguish, interview, question |
| Extended Abstract |
Generalise, predict, evaluate, reflect, hypothesise, create, prove, plan, justify, argue, compose, prioritise, design, construct, perform |
Verbs typical of each level in SOLO Taxonomy
My alignment of the verbs with the SOLO levels, is a little different from that suggested by Biggs in Table 2 below.
If you check Biggs and Tang - Figure 5.2. A hierarchy of verbs that may be used to form intended learning outcomes p.79 and table 5.1.Some verbs for ILOs from the SOLO taxonomy p.80 you will see that I have shifted Biggs’ verbs to better suit a classroom based approach. I wanted to make the connection between the verb and the SOLO level explicit – verbs for bringing in loose ideas, verbs for connecting ideas and verbs for extending ideas. For example, when I developed the classroom based approach for use by students as young as five years old - I shifted classify and sequence to relational because it seemed like the process of sequencing and classifying involved students in making connections between ideas. The SOLO relational visual maps and self-assessment rubrics reinforced this. I moved predict, conclude, summarise, make a plan to the extended abstract level because they seemed to involve students in looking at connected ideas in a new way. The SOLO extended abstract visual maps and self-assessment rubrics reinforced this.
Prof. John Biggs has recognised the changes I made in the development of a classroom based approach to using SOLO – and given his blessing.
Context is important in aligning verbs to SOLO outcomes in Biggs and Tang (2007) John notes “Some verbs could be either extended abstract or relational, depending on, for example,, the degree of originality or the context in which the verb was deployed: ‘solve a problem’, for example. And whether ‘paraphrase’ is relational or multistructural depends on how the student goes about paraphrasing: replacing with like-meaning phrases or rethinking the meaning of the whole text and rewriting it.” Biggs and Tang p80
Table 2: Verbs/Task Descriptors Typical of each Level in SOLO Taxonomy
| SOLO Levels | Source – Biggs Website | Source - Biggs and Tang
Fig. 5.2 p.79 |
Source - Biggs and Tang
Table 5.1 p.80 |
Classroom based approach
Source - Hooked on Thinking Wiki -SOLO Diagram and text http://pamhook.com/wiki/The_Learning_Process |
Classroom based approach
Source - HookED Handouts and Presentations Publications - SOLO Verbs www.pamhook.com |
Classroom based approach
Source – HookED Learning Intention Generator
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unistructural |
Identify, name, follow a simple procedure |
Identify, do simple procedure |
Memorise, identify, recognise, count, define, draw, find, label, match, name, quote, recall, recite, order, tell, write, imitate. |
Define, identify, do simple procedure |
Define, identify, name, draw, find, label, match |
Define, name, find, match, identify draw, label recall |
| Multistructural |
Combine, describe, enumerate, perform serial skills, list |
Enumerate, describe, list, combine, do algorithm |
Classify, describe, list, report, discuss, illustrate, select, narrate, compute, sequence, outline, separate |
Define, describe, do algorithm, combine |
Describe, list, outline, follow a procedure |
Describe, list, outline, follow a procedure |
| Relational |
Analyse, apply, argue, compare and contrast, criticise, explain causes, relate, justify |
Compare, contrast, explain causes, analyse, relate, apply. |
Apply, integrate, analyse, explain, predict, conclude, summarise (précis), review, argue, transfer, make a plan, characterise, compare, contrast, differentiate, organise, debate, make a case, construct, review and rewrite, examine, translate, paraphrase, solve a problem |
Compare, contrast, explain causes, sequence, classify, analyse (part whole), relate, analogy, apply, formulate questions |
Sequence, classify, compare and contrast, explain causes, explain effects, analyse, make an analogy, organise, distinguish, interview, question |
Sequence, compare and contrast, explain effects, make an analogy. distinguish, question, classify, explain causes analyse, organise, interview, apply |
| Extended Abstract |
Create, formulate, generate, hypothesise, reflect, theorise |
Theorise, generalise, hypothesise, reflect |
Compose, invent, originate, prove from first principles, make an original case, solve from first principles |
Evaluate, theorise, generalise, predict, create, imagine |
Generalise, predict, evaluate, reflect, hypothesise, create, prove, plan, justify, argue, compose, prioritise, design, construct, perform |
Generalise, evaluate, hypothesise, prove, justify, compose, design, perform, predict, reflect, create, plan, argue, prioritise, construct, invent
|
SOLO Visual Maps
Visual mapping helps students understand the process steps when they are using academic language - describing, explaining, analysing , evaluating etc. They are useful draft writing templates for both structure and content across different levels of SOLO tasks and outcomes.
When introducing the SOLO maps to students work with familiar content and contexts to reduce the cognitive load when learning a new process. Work for student fluency in map use. Give students many opportunities to use each map so they can "overlearn" the process steps for comparison, explanation etc. Encourage double processing whereby the student drafts thinking using the maps before writing AND also reads content from an existing text/paragraph and then summarise it onto a map. In time fluent users will be able to select an appropriate SOLO process map for an identified task.
Expert users will adapt and modify existing process maps to connect their draft thinking outcomes. For example - connecting a SOLO Explain effects map to a SOLO Sequence map.
Students can also be encouraged to build their own maps using the rectangle/speech bubble/thought bubble templates - as shown in this post
A3 Poster - HOT SOLO Map Overview Download here
File:HookEDHOTMapsWordPoster A3 1.pdf
Check out the following SOLO maps, self assessment rubrics and examples of student use:
The HOT SOLO Maps are published in SOLO Taxonomy - A Guide for Schools Book 1. Summary versions are available in the links above.
The HookED SOLO Maps are published here and in the following presentations.
Hook, P. and Cassé, B. (2013). Taxonomy in the Early Years. Making connections for belonging, being and becoming. Essential Resources Educational Publishers Limited. New Zealand.
McNeill, L. and Hook, P. (2012). SOLO Taxonomy and Making Meaning. Book 1. Text purposes, audiences and ideas. Essential Resources Educational Publishers Limited. New Zealand.
McNeill, L. and Hook, P. (2012). SOLO Taxonomy and Making Meaning. Book 2. Language features, structure and organisation. Essential Resources Educational Publishers Limited. New Zealand.
McNeill, L. and Hook, P. (2012). SOLO Taxonomy and Making Meaning. Book 3. Extended texts and thematic studies. Essential Resources Educational Publishers Limited. New Zealand.
Setting SMART Goals
| Key Attributes of SMART Goals | Develop by ... | Use SOLO Taxonomy ... |
|---|---|---|
| Specific | Ask explicit focused questions. e.g. 5W and 1H questions | Ask questions aligned to differentiated SOLO outcomes. E.g. Compare and contrast (Relational Outcome) |
| Measurable | Establish specific criteria for measuring progress and knowing when a goal has been achieved. | Establish SOLO differentiated success criteria for learning verbs. E.g. HOT SOLO Self assessment rubrics for learning verbs |
| Attainable | Develop differentiated sub-goals | Establish SOLO differentiated success criteria for learning verbs. E.g. HOT SOLO Self assessment rubrics for learning verbs |
| Realistic | Able and motivated to achieve | Use SOLO differentiated success criteria to establish level of pre-topic learning. |
| Timely | Create timeline/Gantt chart | Use SOLO differentiated success criteria for time management (Functioning knowledge) |